When you connect to the VPN (Virtual Private Network), your computer establishes an encrypted link to CAEDM and becomes part of the BYU campus network. You are able to access network resources as if your computer was plugged-in to the university network.
Contents
Quick Installation Facts (for the impatient)
IKEv2 VPN Connections
Servername: vpn.et.byu.edu Protocol: IKEv2 Authentication: EAP-MSCHAPv2
SSL VPN Connections
Download FortiClient after logging into https://vpn.et.byu.edu, or download from http://www.forticlient.com Servername: vpn.et.byu.edu Protocol: SSL VPN
Clientless SSL VPN Connections
Go to https://vpn.et.byu.edu using your browser of choice.
When to use the VPN
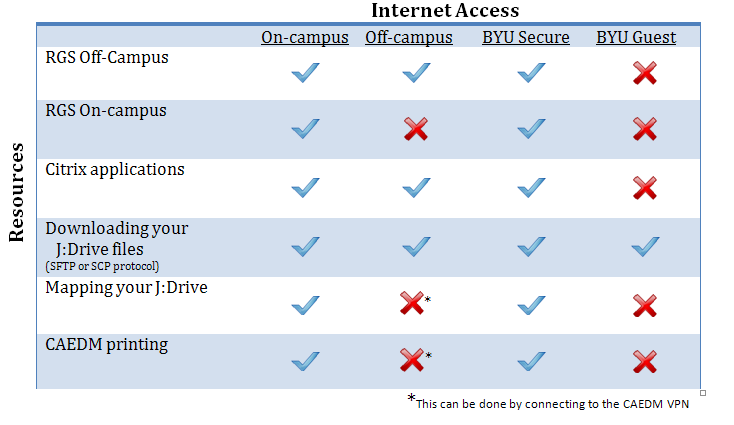
Most CAEDM remote computing resources can be used from off-campus without using the VPN .
However, there are some resources which, for security or licensing reasons, are only available to on-campus machines. When connected to the VPN, your computer is considered part of the on-campus network, thus making these restricted resources available to you remotely, and in a secure fashion.
Examples of such restricted resources you might use remotely include:
- Workstations used by researchers, faculty, and staff
- License servers
- Free access to the Lee library's subscription services (e.g. Compendex, EBSCO, RefWorks, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, and Proquest Safari Books nline)
- Content-filtered Internet access
- Any other campus computer or service protected from the public Internet
As seen in the table above, the VPN will allow off-campus connections to use your J Drive, or to print from off-campus to a CAEDM lab printer. It can also be used with publicly available services, such as RGS, Citrix, or SSH, though these services are already encrypted, so the VPN connection is not necessary. Note that while the VPN will give you wider access to services while on BYU-Guest, it will not remove the bandwidth limitations of BYU-Guest. If you want faster access, use BYU-Secure instead.
VPN Connection Options
There are three ways of connecting to the college VPN, listed in order of general preference:
- IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2)
- SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network)
- Clientless SSL VPN
Each has its own strengths, which are described below.
- IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2)
- IKEv2 is the preferred VPN connection as it is the simplest to use on most operating systems. IKEv2 support is included in Windows 7 or higher, and is available by plug-in or client download for Linux, Android, iOS, and Mac OS X. Unfortunately, Mac OS X also requires a workaround each time you connect and disconnect with the VPN. IKEv2 may have problems connecting in large, crowded conferences centers due to heavy traffic congestion. In such situations the SSL VPN has better success connecting.
- SSL VPN
- SSL VPN may be needed if the Internet Provider you are using doesn't allow IKEv2 VPN connections, or if you are in a heavily crowded conference room. The SSL VPN client is available as a download for Windows, Mac OS X, iOS, and Android.
- Clientless SSL VPN
- The Clientless SSL VPN is best when you can't install or configure the software needed for the IKEv2 or SSL VPN options (e.g. you are using an older version of Mac OS X, or someone else's computer). It requires only a web browser for services like SMB/CIFS (the J: drive) and content-filtered web browsing. A Flash or Java plug-in may be required for other services like SSH. The browser-based experience is not as seamless as the full SSL VPN client, but it can still be useful in a pinch.
Setup and Connection Instructions
VPN Instructions for Windows 7
VPN Instructions for Windows 8
Client-less SSL VPN
The client-less SSL VPN is not as transparent as when using the FortiClient, but can still be useful in a pinch. Once logged in, there are several "Connection Tools" that allow you to connect to a few services, such as the J: drive using the SMB/CIFS tool, or a web site using the HTTP/HTTPS tool. Other Connection Tools may require additional browser plug-ins to work, such as the Citrix client that requires the Java plug-in.
To connect to the Client-less CAEDM SSL VPN:
- Using your web browser, go to "https://vpn.et.byu.edu".
- Login to the blue CAEDM Client-less SSL VPN screen.
- NOTE: If you get an orange login screen then you have entered the wrong address and you will not be able to login.
You are now connected to the Client-less SSL VPN, and may use the displayed Connection Tools.
To disconnect from the Client-less CAEDM SSL VPN:
- On the CAEDM Client-less SSL VPN screen, click "Logout".
You are now disconnected from the Client-less SSL VPN.
Troubleshooting
- If you are going to be using programs installed on your local computer that require a licence server, make sure that you include the et.byu.edu extension.
Example: Wizbang 2000 requires a licence server to run. Normally, that licence server would be set to something like "1234@licserv", when using the VPN, it needs to be "1234@licserv.et.byu.edu". This will route the licence request through VPN, and will then be able to find the licence server. You can add the et.byu.edu and it will work just fine on campus as well, in addition to off-campus locations.
- Do not use split tunnelling.